Digital twin technology, which involves creating a real-time digital replica of a physical system, has gained significant traction in water management for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and optimizing operations
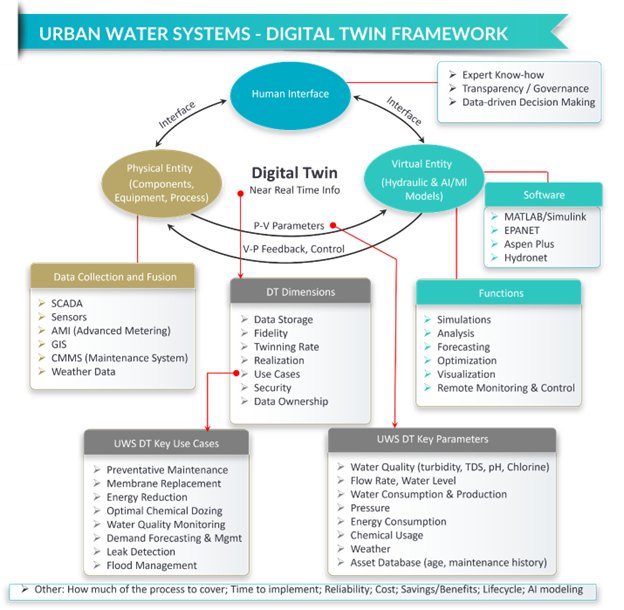

Digital twin technology, which involves creating a real-time digital replica of a physical system, has gained significant traction in water management for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and optimizing operations
Water filtration is essential to providing safe drinking water, especially as global demand rises and water sources become increasingly contaminated. Advanced filtration methods like reverse osmosis (RO), ultraviolet (UV) treatment, […]
Water scarcity is a pressing issue affecting billions worldwide, with impacts that span from agricultural productivity to public health and economic stability. Addressing this challenge requires robust and reliable indicators to quantify water scarcity, assess resource availability, and guide sustainable water policies
The water-energy nexus illustrates the interconnectedness of two critical resources, where reducing water usage directly impacts energy conservation
Microplastics and emerging contaminants, such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals, are increasingly found in water sources and present significant risks to ecosystems and human health.
Desalination offers a viable option for addressing global water scarcity, particularly in arid and drought-prone regions. With recent technological advancements, desalination is becoming increasingly energy-efficient and environmentally conscious
Groundwater resources are crucial to global water security, supplying 25-30% of global freshwater demand (WWAP, 2020). However, excessive groundwater extraction has led to severe depletion, with significant socio-economic and environmental consequences.
Climate change has significant implications for the global water cycle, affecting precipitation patterns, snowmelt, evaporation rates, and groundwater recharge. These changes exacerbate water scarcity in vulnerable regions and create challenges for managing freshwater resources sustainably.
Agriculture accounts for approximately 70% of global freshwater withdrawals (FAO, 2019), and improving water efficiency in this sector is essential for sustainable water management. Advances in precision irrigation, soil moisture sensors, and water-saving techniques offer promising solutions for reducing agricultural water demand.
Drought-resistant crops offer a promising solution for conserving water and sustaining yields in arid regions. Advances in genomics and biotechnology allow scientists to develop crop varieties that require less water and can withstand prolonged dry conditions.
Water recycling, specifically greywater and blackwater reuse, is becoming essential for sustainable water management, particularly in water-scarce regions. Recycling these wastewater types offers both environmental benefits and water savings.